LiFeAs体系中实现大面积、高度有序和可调控的“马约拉纳零能模‘格点阵列’”
(Ordered and tunable Majorana-zero-mode lattice in naturally-strained LiFeAs )
M. Li, G. Li, L. Cao, X. T. Zhou, X. C. Wang, C. Q. Jin, C.-K. Chiu, S. J. Pennycook, Z. Q. Wang, H.-J. Gao
Nature 606, 890 (2022)
Highlight: 中科院(CAS), 中科院物理所(IOP)
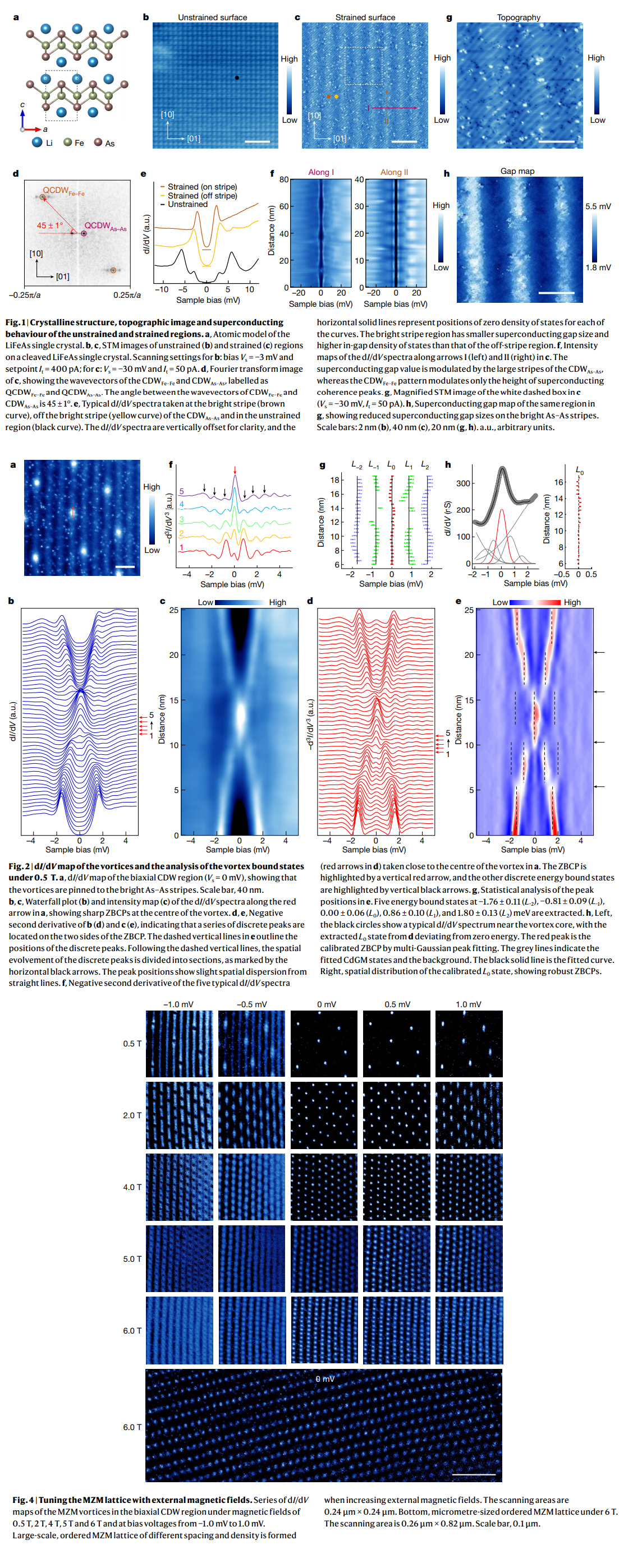
Majorana zero modes (MZMs) obey non-Abelian statistics and are considered building blocks for constructing topological qubits. Iron-based superconductors with topological band structures have emerged as promising hosting materials, because isolated candidate MZMs in the quantum limit have been observed inside the topological vortex cores. However, these materials suffer from issues related to alloying induced disorder, uncontrolled vortex lattices 10–13 and a low yield of topological vortices. Here we report the formation of an ordered and tunable MZM lattice in naturally strained stoichiometric LiFeAs by scanning tunneling microscopy/ spectroscopy. We observe biaxial charge density wave (CDW) stripes along the Fe–Fe and As–As directions in the strained regions. The vortices are pinned on the CDW stripes in the As–As direction and form an ordered lattice. We detect that more than 90?per?cent of the vortices are topological and possess the characteristics of isolated MZMs at the vortex center, forming an ordered MZM lattice with the density and the geometry tunable by an external magnetic field. Notably, with decreasing the spacing of neighboring vortices, the MZMs start to couple with each other. Our findings provide a pathway towards tunable and ordered MZM lattices as a platform for future topological quantum computation.