有机超导体K3C22H14的结构及超导性质
(Structure and magnetic property of potassium intercalated pentacene: observation of superconducting phase in KxC22H14)
T. Nakagawa, Z. Yuan, J. Zhang, K. V. Yusenko, C. Drathen, Q. Q. Liu, S. Margadonna and C. Q. Jin
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 28, 484001 (2016)
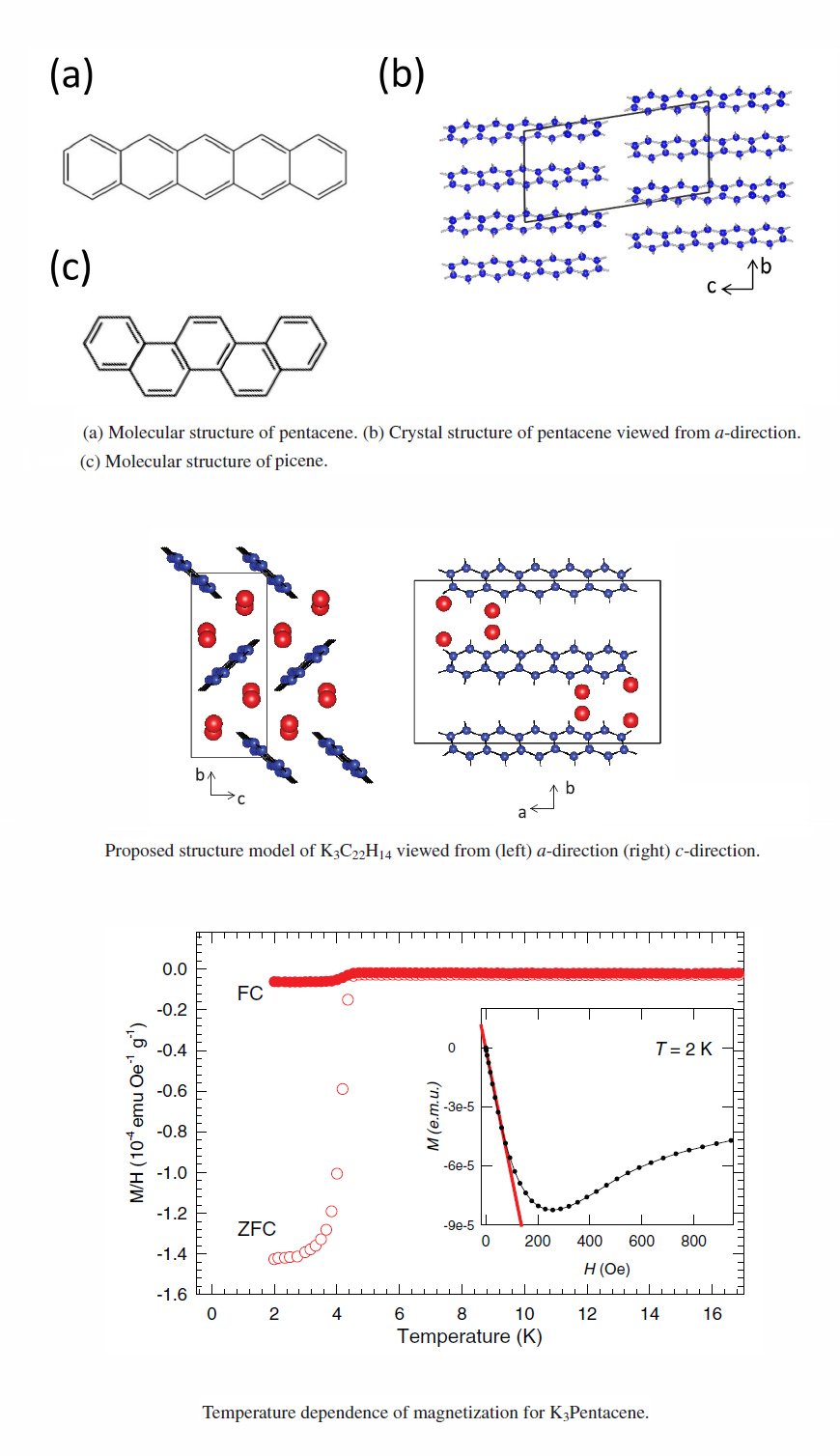
We report the results from systematic investigations on the structure and magnetic properties of potassium intercalated pentacene as a function of potassium content, KxC22H14 (1< x < 3). Synchrotron radiation powder x-ray diffraction technique revealed that there are two different stable phases can be obtained via potassium intercalation, namely, K1C22H14 phase and K3C22H14 phase. Structural phase transition was induced when the potassium content was increased to the nominal value x = 3. This phase transition is accompanied by drastic change in their magnetic property, where those samples with compositions K1C22H14 shows ferromagnetic behavior and those with near K3C22H14 lead to observation of superconductivity with transition temperature, Tc, of 4.5 K. It is first time that superconductivity was observed in linear oligoacenes. Both magnetization study and synchrotron radiation powder x-ray diffraction clearly indicates that the superconducting phase belong to K3C22H14 as a result of phase transition from triclinic to monoclinic structure induced by chemical doping.