压力诱导的拓扑超导
(Pressure-induced superconductivity in topological parent compound Bi2Te3)
J. L. Zhang, S. J. Zhang, H. M. Weng, W. Zhang, L. X. Yang, Q. Q. Liu, S. M. Feng, X. C. Wang, R. C. Yu, L. Z. Cao, L. Wang, W. G. Yang, H. Z. Liu, W. Y. Zhao, S. C. Zhang, X. Dai, Z. Fang, C. Q. Jin
Be online in Dec. 2010 with the doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014085108
Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. (PNAS) 108, 24 (2011)
自然界中物质按照导电性可分为金属、绝缘体、半导体等,拓扑绝缘体指这样的一类新的物质状态,它的体态为绝缘体而表(界)面态为金属。这种表(界)面金属态受时间反演不变的保护,为材料内禀特性而和具体结构无关,金属态对杂质散射等外界作用非常稳定。拓扑超导指在保持材料的拓扑属性的前提下实现的超导转变,在拓扑超导界面具有无质量的Majorana准粒子,这可能成为设计新一代量子计算机重要途径。
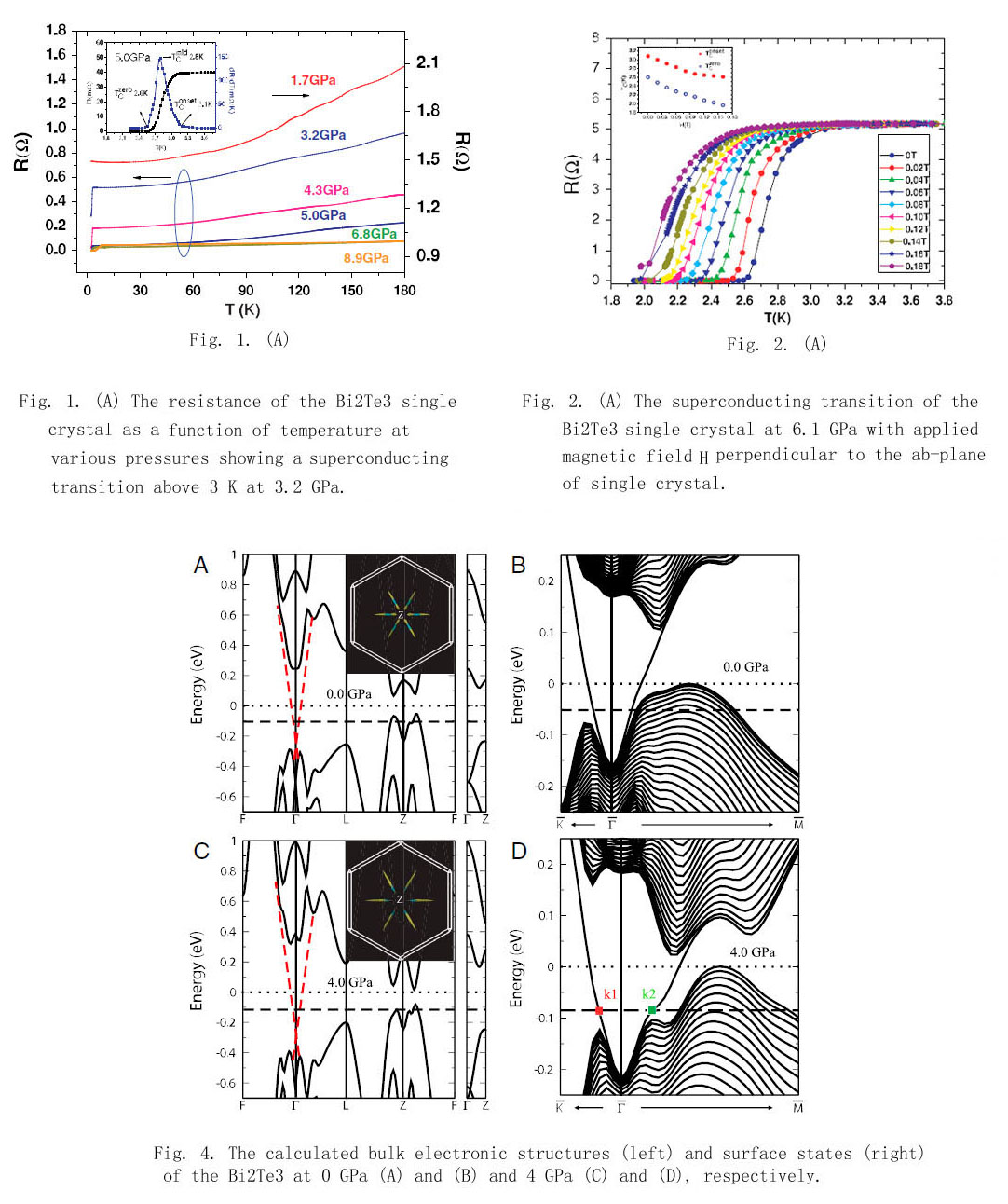
本工作在理论预言的三维拓扑化合物Bi2Te3中观察到在(3~6GPa)压力诱导的超导转变,结构实验表明在上述压力区间Bi2Te3依然保持常压相构型,第一性原理计算表明母体相依然具有拓扑属性。Hall系数测量表明P型导电,基于以上的物性和结构实验及理论计算,在Bi2Te3单晶中观察到的压力诱导的超导转变和拓扑属性密切关联。
物理所的科研动态和中科院的科研进展中分别对该工作进行报道。该工作于2012年12月被评为“中国百篇最具影响国际学术论文”。
We report a successful observation of pressure-induced superconductivity in a topological compound Bi2Te3 with Tc of ~3 K between 3 to 6 GPa. The combined high-pressure structure investigations with synchrotron radiation indicated that the superconductivity occurred at the ambient phase without crystal structure phase transition. The Hall effects measurements indicated the holetype carrier in the pressure-induced superconducting Bi2Te3 single crystal. Consequently, the first-principles calculations based on the structural data obtained by the Rietveld refinement of X-ray diffraction patterns at high pressure showed that the electronic structure under pressure remained topologically nontrivial. The results suggested that topological superconductivity can be realized in Bi2Te3 due to the proximity effect between superconducting bulk states and Dirac-type surface states. We also discuss the possibility that the bulk state could be a topological superconductor.