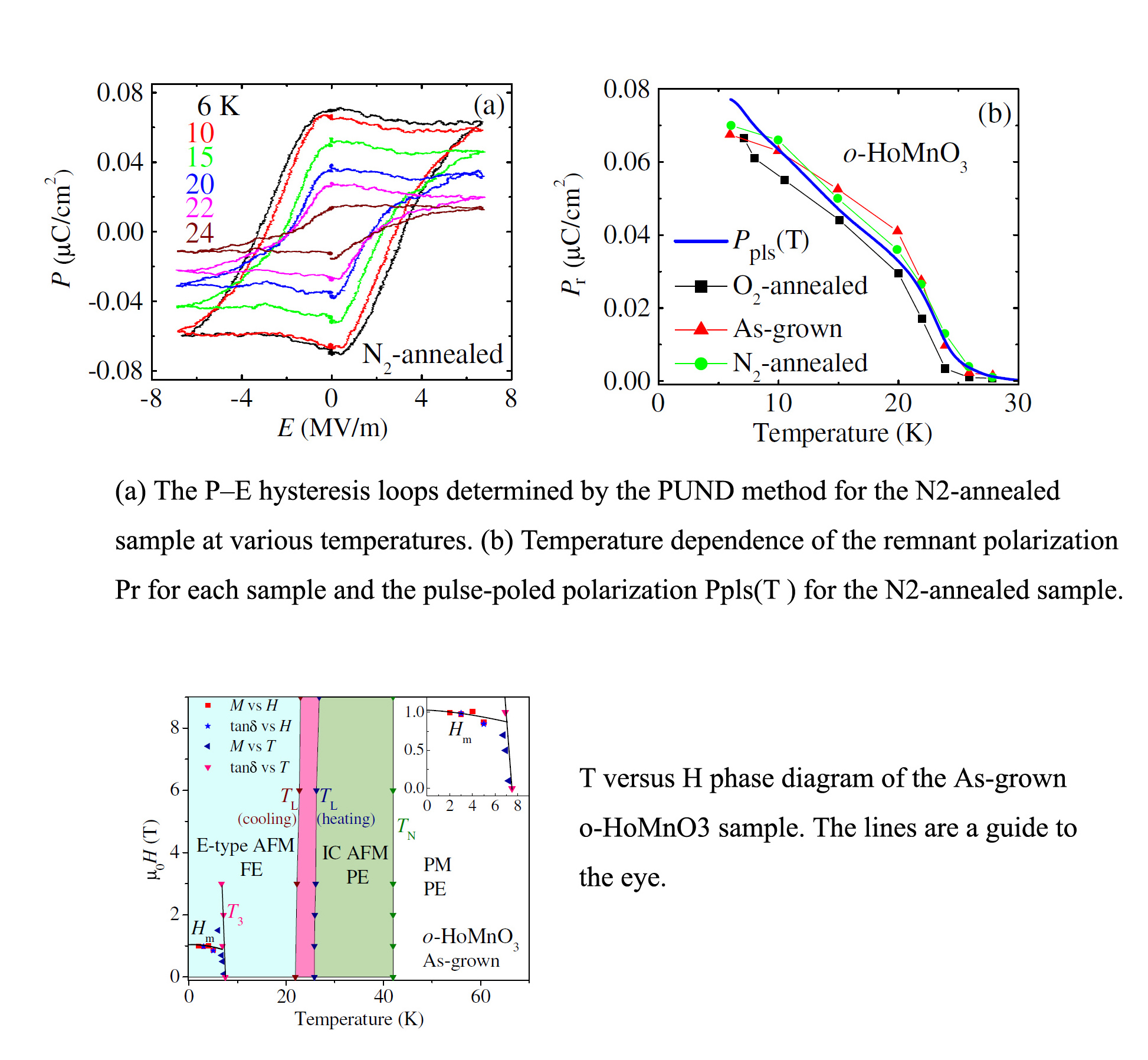
在正交相HoMnO3材料中得到最高本征铁电极化
(Determination of the intrinsic ferroelectric polarization in orthorhombic HoMnO3)
S.M. Feng, Y.S. Chai, J.L. Zhu, N. Manivannan, Y.S. Oh, L.J. Wang, Y.S. Yang, C.Q. Jin and Kee Hoon Kim
New J. Phys. 12, 073006 (2010)
Whether or not a large ferroelectric polarization P exists in the orthorhombic HoMnO3 with E-type antiferromagnetic spin ordering remains one of the unresolved, challenging issues in the physics of multiferroics. The issue is closely linked to an intriguing experimental difficulty in determining the P of polycrystalline specimens, namely that conventional pyroelectric current measurements performed after a poling procedure under high dc electric fields are subject to large errors due to the problems caused by leakage currents or space charges. To overcome the difficulty, we employed the positive-up negative-down (PUND) method, which uses successively the two positive and two negative electrical pulses, to directly measure electrical hysteresis loops in several polycrystalline HoMnO3 specimens below their Néel temperatures. We found that all the HoMnO3 samples had similar remnant polarization Pr values at each temperature, regardless of their variation in resistivity, dielectric constant and pyroelectric current levels. Moreover, the Pr value of ~0.07μC cm?2 at 6K is consistent with the P value obtained from the pyroelectric current measurement performed after a short pulse poling. Our findings suggest that the intrinsic P of polycrystalline HoMnO3 can be determined through the PUND method and P at 0K may reach ~0.24μC cm?2 in a single crystalline specimen. This P value is still much smaller than the theoretically predicted one but is one of the largest observed in magnetism induced ferroelectrics.